
In marketing research, it is the questionnaire that ensures that the research objectives are met. That is why the questionnaire must be such that it meets the intended purpose.
What is a Questionnaire?
- All techniques of data collection in which each person is asked to respond to the same set of questions in a predetermined order.
- Most widely used data collection technique
- More appropriate for descriptive, explanatory research
Evaluating Questionnaires (Pros & Cons)
Pros:
- Inexpensive to administer
- Quick to administer
- Absence of interview effects/bias
- No interviewer variability
- Convenience for respondents
Cons:
- Cannot prompt/probe
- Difficulty of respondents understanding questions
- Questionnaire can be looked at as a whole first
- Lack of control of sample
- Cannot collect additional data
- Partially answered questions
- Not suitable for all types of respondents
When to Use Questionnaires
- Not a good choice for exploratory research that requires large number of open ended questions;
- Questionnaires work best with standardised questions that can be interpreted in the same way by all respondents;
- Tend to be used for descriptive or explanatory research, e.g., attitude, opinion-based, to explain relationships between variables, or cause- and- effect relationships
Questionnaires are used in the following research strategies: Survey, Experiment, Case study
Types of questionnaire
Types of questionnaire:
Self-administered
– Internet and Intranet-mediated questionnaires
– Delivery and collection questionnaire
– Postal questionnaire
Interviewer – administered
– Telephone questionnaire
– Structured interview
Choice of questionnaire
The choice of questionnaire will be influenced by a determined number of factors:
- Characteristics of the respondents from whom you wish to collect data
Importance of reaching a particular person as respondent - Importance of respondents answers not being contaminated or distorted
- Size of sample you require for your analysis, taking into account the likely response rate
- Types of questions you need to ask to collect your data
- Number of questions you need to ask to collect your data
- Time available to complete the data collection
- Financial implications of data collection and entry
- Availability of interviewers and field workers to assist
Sampling methods
Two main types:
- Probability sampling: This implies a random sample has been used
- Non-probability sampling: Convenience; Snowball sampling; Quota sampling
Before designing a questionnaire
You need:
- To have identified your DV and IVs (i.e. the variables to be examined in the study);
- Have written by hypothesis;
- Ideally have an idea of the statistical tests you want to perform from the data;
Designing Questionnaires
Procedure for Developing a Questionnaire
- Specify What Information Will Be Sought
- Determine Method of Administration
- Determine Content of Individual Questions
- Determine Form of Response to Each Question
- Determine Wording of Each Question
- Determine Question Sequence
- Determine Physical Characteristics of Questionnaires
- Develop Recruiting Message or Script
- Reexamine Steps 1-7 and Revise If Necessary
- Pretest Questionnaire and Revise If Necessary
When designing a questionnaire make sure you have different types of variables in your questions- e.g. have some ordinal, nominal, interval, etc.
Because it gives you more variety of data for STATISTICAL TESTING
Principles in designing questionnaires
- Do not cramp the presentation
- Clear instructions about how to respond
- Each item should express one idea
- Avoid jargons
- Use simple expressions
- Logical flow of questions
Rules for designing questionnaires
- Always bear in mind the research question
- What do you want to know?
- How would you answer it?
- Avoid ambiguous terms in questions (e.g. often, regularly)
- Avoid long questions
- Avoid double-barrelled questions (e.g. how satisfied are you with pay and conditions in your job?)
- Avoid leading questions (e.g. do you think that UK corporate directors receive excessive financial compensation?)
- Avoid the use of negatives (e.g. Do you agree with the view that students should not have to take out loans to finance higher education)
- Avoid technical terms
- Does the respondent have the requisite knowledge?
- Offer a no opinion option
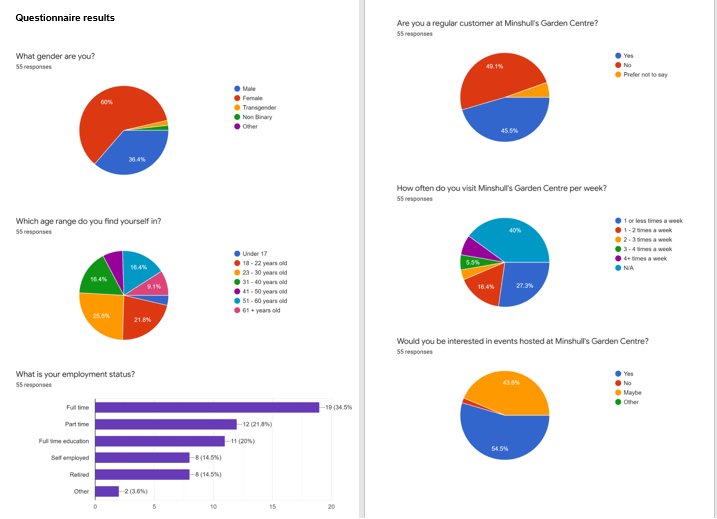
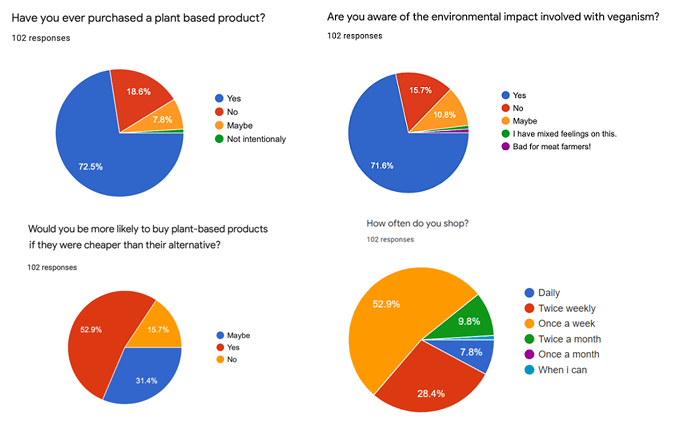
Analyzing Questionnaire Results

Leave a Reply